Annihilation of calcium oscillations with PLC activation inhibition: Difference between revisions
JonasSchulze (talk | contribs) m Text replacement - "<bibreferences/>" to "<biblist />" |
JonasSchulze (talk | contribs) m Text replacement - "\<bibref\>(.*)\<\/bibref\>" to "<bib id="$1" />" |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
== Reference Solutions == | == Reference Solutions == | ||
A solution for this problem is described in < | A solution for this problem is described in <bib id="Lebiedz2005" />. A local minimum that is actually slightly worse than the solution provided for only one control, is shown in the next plots. | ||
<gallery caption="Reference solution plots" widths="180px" heights="140px" perrow="2"> | <gallery caption="Reference solution plots" widths="180px" heights="140px" perrow="2"> | ||
Revision as of 20:30, 30 December 2015
| Annihilation of calcium oscillations with PLC activation inhibition | |
|---|---|
| State dimension: | 1 |
| Differential states: | 4 |
| Discrete control functions: | 2 |
| Interior point equalities: | 4 |
This control problem is closely related to Annihilation of calcium oscillations. The only difference is an additional control function, the inhibition of PLC activation. We state only the differences in this article.
Mathematical formulation
For almost everywhere the mixed-integer optimal control problem is given by
Note that we write instead of and have an additional control function . The regularization parameters are set to .
Reference Solutions
A solution for this problem is described in [Lebiedz2005]Author: Lebiedz, D.; Sager, S.; Bock, H.G.; Lebiedz, P.
Journal: Physical Review Letters
Pages: 108303
Title: Annihilation of limit cycle oscillations by identification of critical phase resetting stimuli via mixed-integer optimal control methods
Volume: 95
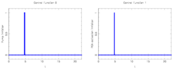
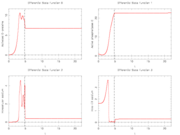
Year: 2005 . A local minimum that is actually slightly worse than the solution provided for only one control, is shown in the next plots.
. A local minimum that is actually slightly worse than the solution provided for only one control, is shown in the next plots.
- Reference solution plots
-
Optimal stimuli determined by mixed-integer optimal control.
-
Corresponding differential states.
Variants
References
| [Lebiedz2005] | Lebiedz, D.; Sager, S.; Bock, H.G.; Lebiedz, P. (2005): Annihilation of limit cycle oscillations by identification of critical phase resetting stimuli via mixed-integer optimal control methods. Physical Review Letters, 95, 108303 |  |