Difference between revisions of "Bioreactor"
TobiasWeber (Talk | contribs) (→Reference Solution) |
TobiasWeber (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
<gallery caption="Reference solution" widths="271px" heights="379px" perrow="2"> | <gallery caption="Reference solution" widths="271px" heights="379px" perrow="2"> | ||
| + | [[File:Example.jpg]] | ||
Image:| Optimal solution for the ACADO example. | Image:| Optimal solution for the ACADO example. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 15:27, 9 December 2015
The bioreactor example is an easy bioreactor with an substrate that is converted to a product by the biomass in the reactor. It has three states and a control that is describing the feed concentration of substrate. It is taken from the examples folder of the ACADO toolkit described in:
Houska, Boris, Hans Joachim Ferreau, and Moritz Diehl. "ACADO toolkit—An open‐source framework for automatic control and dynamic optimization." Optimal Control Applications and Methods 32.3 (2011): 298-312.
Originally the problem seems to be motivated by:
VERSYCK, KARINA J., and JAN F. VAN IMPE. "Feed rate optimization for fed-batch bioreactors: From optimal process performance to optimal parameter estimation." Chemical Engineering Communications 172.1 (1999): 107-124.
Contents
Model Formulation
The dynamic model is an ODE model:
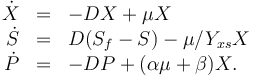
The three states describe the concentration of the biomass ( ), the substrate (
), the substrate ( ), and the product (
), and the product ( ) in the reactor. In steady state the feed and outlet are equal and dilute all three concentrations with a ratio
) in the reactor. In steady state the feed and outlet are equal and dilute all three concentrations with a ratio 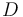 . The biomass grows with a rate
. The biomass grows with a rate
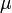 , while it eats up the substrate with the rate
, while it eats up the substrate with the rate 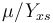 and produces product at a rate
and produces product at a rate 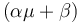 . The rate
. The rate 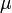 is given by:
is given by:
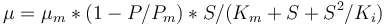
The fixed parameters (constants) of the model are as follows.
| Name | Symbol | Value | Unit |
| Dilution | 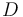
|
0.15 | [-] |
| Rate coefficient | 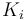
|
22 | [-] |
| Rate coefficient | 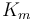
|
1.2 | [-] |
| Rate coefficient | 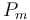
|
50 | [-] |
| Substrate to Biomass rate | 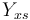
|
0.4 | [-] |
| Linear slope | 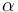
|
2.2 | [-] |
| Linear intercept | 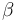
|
0.2 | [-] |
| Maximal growth rate | 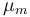
|
0.48 | [-] |
Optimal Control Problem
Writing shortly for the states in vector notation 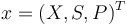 the OCP reads:
the OCP reads:
![\begin{array}{cl}
\displaystyle \min_{x,S_f} & J(x,S_f)\\[1.5ex]
\mbox{s.t.} & \dot{x} = f(x,S_f), \forall \, t \in [0,48]\\
& x(0) = (6.5,12,22)^T \\
& x \in \R^3,\,S_f \in [28.7,40].
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/8/f/a/8faa15c9069ea63b2a4359012e47ea77.png)
Objective
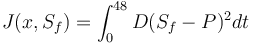
Reference Solution
Here we first give the reference solution according to the ACADO example. In the next section the C++ source code for this solution is given.
- Reference solution
Source Code
In this section one can provide the source code of the implementation, that solved the problem and produced the reference solution. This should be done by providing source files.