Difference between revisions of "Lotka Volterra absolute fishing problem"
ClemensZeile (Talk | contribs) |
ClemensZeile (Talk | contribs) (→Reference Solutions) |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
<gallery caption="Reference solution plots" widths="180px" heights="140px" perrow="2"> | <gallery caption="Reference solution plots" widths="180px" heights="140px" perrow="2"> | ||
| − | Image: | + | Image:Lotka_abs_fish_relaxed_12000_80.pdf| Optimal relaxed controls and states determined by an direct approach with ampl_mintoc (Radau collocation) and <math>n_t=12000, \, n_u=150</math>. |
| − | Image: | + | Image:Lotka_abs_fish_CIA_states_12000_80.pdf| Differential states determined by an direct approach (Radau collocation) with ampl_mintoc and <math>n_t=12000, \, n_u=150</math>. The relaxed controls were approximated by Combinatorial Integral Approximation. |
| + | Image:Lotka_abs_fish_CIA_controls_12000_80.pdf| Binary control determined by an direct approach (Radau collocation) with ampl_mintoc and <math>n_t=12000, \, n_u=150</math>. The relaxed controls were approximated by Combinatorial Integral Approximation. The fishing control shows a lot of chattering. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 13:10, 14 October 2019
| Lotka Volterra absolute fishing problem | |
|---|---|
| State dimension: | 1 |
| Differential states: | 3 |
| Discrete control functions: | 5 |
| Interior point equalities: | 3 |
This site describes a Lotka Volterra variant with five binary controls that all represent fishing of an absolute biomass.
Mathematical formulation
The mixed-integer optimal control problem is given by
![\begin{array}{llclr}
\displaystyle \min_{x, w} & x_2(t_f) \\[1.5ex]
\mbox{s.t.}
& \dot{x}_0 & = & x_0 - x_0 x_1 - \; \sum\limits_{i=1}^{5} c_{0,i}\; w_i, \\
& \dot{x}_1 & = & - x_1 + x_0 x_1 - \; \sum\limits_{i=1}^{5} c_{1,i}\; w_i, \\
& \dot{x}_2 & = & (x_0 - 1)^2 + (x_1 - 1)^2, \\[1.5ex]
& x(0) &=& (0.5, 0.7, 0)^T, \\
& \sum\limits_{i=1}^{5}w_i(t) &=& 1, \\
& w_i(t) &\in& \{0, 1\}, \quad i=1\ldots 5.
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/5/6/1/561f1c30e70fb5e6d77c0387bc2f75d2.png)
Here the differential states 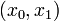 describe the biomasses of prey and predator, respectively. The third differential state is used here to transform the objective, an integrated deviation, into the Mayer formulation
describe the biomasses of prey and predator, respectively. The third differential state is used here to transform the objective, an integrated deviation, into the Mayer formulation 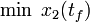 . This problem variant allows to choose between three different fishing options.
. This problem variant allows to choose between three different fishing options.
Parameters
These fixed values are used within the model.
![\begin{array}{rcl}
[t_0, t_f] &=& [0, 12],\\
(c_{0,1}, c_{1,1}) &=& (0.2, 0.1),\\
(c_{0,2}, c_{1,2}) &=& (0.4, 0.2),\\
(c_{0,3}, c_{1,3}) &=& (0.01, 0.1),\\
(c_{0,4}, c_{1,4}) &=& (0, 0),\\
(c_{0,5}, c_{1,5}) &=& (-0.1, -0.2).
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/d/6/f/d6f9204a55f64eec5fc28b1440cf7178.png)
Reference Solutions
If the problem is relaxed, i.e., we demand that  is in the continuous interval
is in the continuous interval ![[0, 1]](https://mintoc.de/images/math/c/c/f/ccfcd347d0bf65dc77afe01a3306a96b.png) rather than being binary, the optimal solution can be determined by means of direct optimal control.
rather than being binary, the optimal solution can be determined by means of direct optimal control.
The optimal objective value of the relaxed problem with 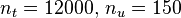 is
is 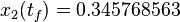 . The objective value of the solution with binary controls obtained by Combinatorial Integral Approximation (CIA) is
. The objective value of the solution with binary controls obtained by Combinatorial Integral Approximation (CIA) is 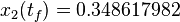 .
.
- Reference solution plots