Car testdrive (lane change manoeuvre)
| Car testdrive (lane change manoeuvre) | |
|---|---|
| State dimension: | 1 |
| Differential states: | 7 |
| Continuous control functions: | 3 |
| Discrete control functions: | 1 |
| Interior point inequalities: | 7 |
The testdrive control problem is a time optimal double lane change maneouvre with gear shift. It has been introduced as a benchmark problem for mixed-integer optimal control by <bibref>Gerdts2005</bibref>.
Contents
[hide]Mathematical formulation
The mathematical equations form a small-scale ODE model.
The vehicle dynamics are based on a single-track model, derived under the simplifying assumption that rolling and pitching of the car body can be neglected. Consequentially, only a single front and rear wheel is modeled, located in the virtual center of the original two wheels. Motion of the car body is considered on the horizontal plane only.
Four controls represent the driver's choice on steering and velocity. We denote with 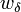 the steering wheel's angular velocity. The force
the steering wheel's angular velocity. The force 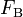 controls the total braking force, while the accelerator pedal position
controls the total braking force, while the accelerator pedal position 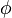 is translated into an accelerating force. Finally, the selected gear
is translated into an accelerating force. Finally, the selected gear 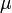 influences the effective engine torque's transmission.
influences the effective engine torque's transmission.
Resulting MIOCP
For ![t \in [t_0, t_f]](https://mintoc.de/images/math/5/5/8/55823791d9100bcb5461801aff4f6edd.png) almost everywhere the mixed-integer optimal control problem is given by
almost everywhere the mixed-integer optimal control problem is given by
![\begin{array}{llcl}
\displaystyle \min_{x(\cdot), u(\cdot), \mu(\cdot)} & t_\text{f} \\[1.5ex]
\mbox{s.t.} & \dot{x}(t) & = & f(t, x(t), u(t), \mu(t)), \\
& x(t_0) &=& x_0, \\
& r(t,x(t),u(t)) &\geq& 0, \\
& \mu(t) &\in& \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5\}.
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/0/0/3/00382d7408dddcf936f8d70afb496034.png)
Parameters
These fixed values are used within the model.
| Symbol | Value | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
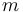 |
1.239e+3 | kg | Mass of the car |
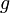 |
9.81 | m/s^2 | Gravity constant |
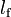 |
1.19016 | m | Front wheel distance to center of gravity |
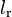 |
1.37484 | m | Rear wheel distance to center of gravity |
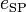 |
0.5 | m | Drag mount point distance to center of gravity |
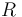 |
0.302 | m | Wheel radius |
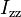 |
1.752e+3 | kg m^2 | Moment of inertia |
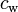 |
0.3 | Air drag coefficient | |
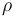 |
1.249512 | kg/m^3 | Air density |
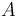 |
1.4378946874 | m^2 | Effective flow surface |
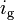 |
3.09, 2.002, 1.33, 1.0, 0.805 | - | Transmission ratios for the five gears |
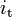 |
3.91 | - | Engine transmission ratio |
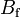 |
1.096e+1 | - | Pacejka coefficients (stiffness) |
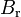 |
1.267e+1 | - | |
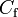 |
1.3 | - | Pacejka coefficients (shape) |
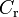 |
1.3 | - | |
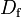 |
4.5604e+3 | - | Pacejka coefficients (peak) |
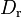 |
3.94781e+3 | - | |
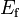 |
-0.5 | - | Pacejka coefficients (curvature) |
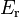 |
-0.5 | - |
Test course
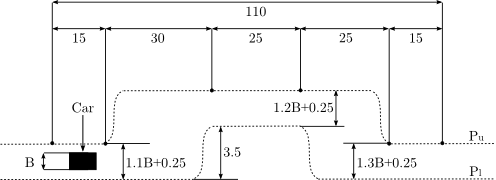
The double-lane change manoeuvre presented in <bibref>Gerdts2005</bibref> is realized by constraining the car's position onto a prescribed track at any time ![t\in[t_0,t_\text{f}]](https://mintoc.de/images/math/e/2/3/e234c61ce225d19679331caf0281c8b0.png) . Starting in the left position with an initial prescribed velocity, the driver is asked to manage a change of lanes modeled by an offset of 3.5 meters in the track. Afterwards he is asked to return to the starting lane. This manoeuvre can be regarded as an overtaking move or as an evasive action taken to avoid hitting an obstacle suddenly appearing on the starting lane.
. Starting in the left position with an initial prescribed velocity, the driver is asked to manage a change of lanes modeled by an offset of 3.5 meters in the track. Afterwards he is asked to return to the starting lane. This manoeuvre can be regarded as an overtaking move or as an evasive action taken to avoid hitting an obstacle suddenly appearing on the starting lane.
From a mathematical point of view, the test track is described by setting up piecewise cubic spline functions 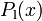 and
and 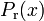 modeling the top and bottom track boundary, given a horizontal position
modeling the top and bottom track boundary, given a horizontal position 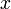 .
.
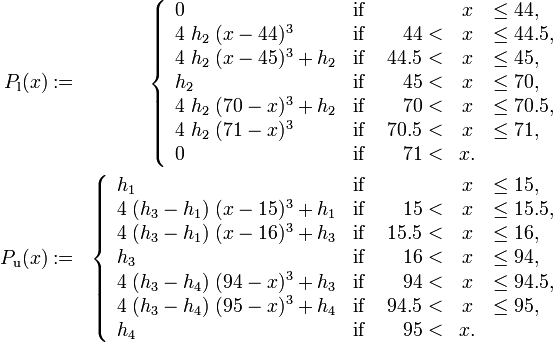
where 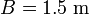 is the car's width and
is the car's width and
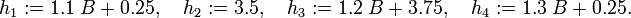
Reference Solutions
Reference solutions for the case of a fixed time-grid are given in <bibref>Gerdts2005</bibref>. Solutions for a non-fixed time grid are given in <bibref>Gerdts2006</bibref>.
Source Code
C
The differential equations in C code:
// Controls double C_steer = u[0]; double C_brake = u[1]; double C_acc = u[2]; // Differential states double X_v = xd[2]; double X_beta = xd[3]; double X_psi = xd[4]; double X_wz = xd[5]; double X_delta = xd[6]; // Intermediate values double alpha_f, alpha_r, v_km_h, v_km_h2; double F_Ax, F_Ay, F_Bf, F_Br, F_Rf, F_Rr, F_sf, F_sr, F_lr, F_lf; double f_R, f_1, w_mot, f_2, f_3, M_mot, M_wheel; double X_v_cos_X_beta, X_v_sin_X_beta; X_v_cos_X_beta = X_v * cos ( X_beta ); X_v_sin_X_beta = X_v * sin ( X_beta ); alpha_f = X_delta - atan( ( P_l_f * X_wz - X_v_sin_X_beta ) / X_v_cos_X_beta ); alpha_r = atan( ( P_l_r * X_wz + X_v_sin_X_beta ) / X_v_cos_X_beta ); F_sf = P_D_f * sin( P_C_f * atan( P_B_f*alpha_f - P_E_f*(P_B_f*alpha_f - atan(P_B_f*alpha_f)) ) ); F_sr = P_D_r * sin( P_C_r * atan( P_B_r*alpha_r - P_E_r*(P_B_r*alpha_r - atan(P_B_r*alpha_r)) ) ); F_Ax = 0.5 * P_c_w * P_rho * P_A * X_v*X_v; F_Ay = 0.0; F_Bf = 2.0/3.0 * C_brake; F_Br = 1.0/3.0 * C_brake; v_km_h = X_v / 100.0 * 3.6; v_km_h2 = v_km_h * v_km_h; f_R = P_f_R0 + P_f_R1 * v_km_h + P_f_R4 * v_km_h2 * v_km_h2; F_Rf = f_R * P_F_zf; F_Rr = f_R * P_F_zr; f_1 = 1.0 - exp( -3.0 * C_acc ); w_mot = X_v * P_ig * P_i_t / P_R; f_2 = -37.8 + (1.54 - 0.0019 * w_mot_i) * w_mot; f_3 = -34.9 - 0.04775 * w_mot; M_mot = f_1 * f_2_i + ( 1.0 - f_1 ) * f_3_i; M_wheel = P_ig * P_i_t * M_mot_i; F_lr = M_wheel / P_R - F_Br - F_Rr; F_lf = - F_Bf - F_Rf; // 0 Horizontal position x rhs[0] = X_v * cos( X_psi - X_beta ); // 1 Vertical position y rhs[1] = X_v * sin( X_psi - X_beta ); // 2 Velocity v rhs[2] = 1.0 / P_m * ( (F_lr - F_Ax) * cos(X_beta) + F_lf * cos(X_delta + X_beta) - (F_sr - F_Ay) * sin(X_beta) - F_sf * sin(X_delta + X_beta) ); // 3 Side slip angle beta rhs[3] = X_wz - 1.0 / (P_m * X_v) * ( (F_lr - F_Ax) * sin(X_beta) + F_lf * sin(X_delta + X_beta) + (F_sr - F_Ay) * cos(X_beta) + F_sf * cos(X_delta + X_beta) ); // 4 Yaw angle psi rhs[4] = X_wz; // 5 Velocity of yaw angle w_z rhs[5] = 1.0 / P_I_zz * ( F_sf * P_l_f * cos(X_delta) - F_sr * P_l_r + F_lf * P_l_f * sin(X_delta) - F_Ay * P_e_SP ); // 6 Steering angle delta rhs[6] = C_steer;
Variants
See testdrive overview page.
References
<bibreferences/>