Hanging chain problem (GEKKO)
From mintOC
This page contains a solution of the energy minimization of the Hanging chain problem in GEKKO Python format. The GEKKO package is available with pip install gekko. The Python code uses orthogonal collocation and a simultaneous optimization method. The end point constraints are imposed as soft constraints (objective terms).
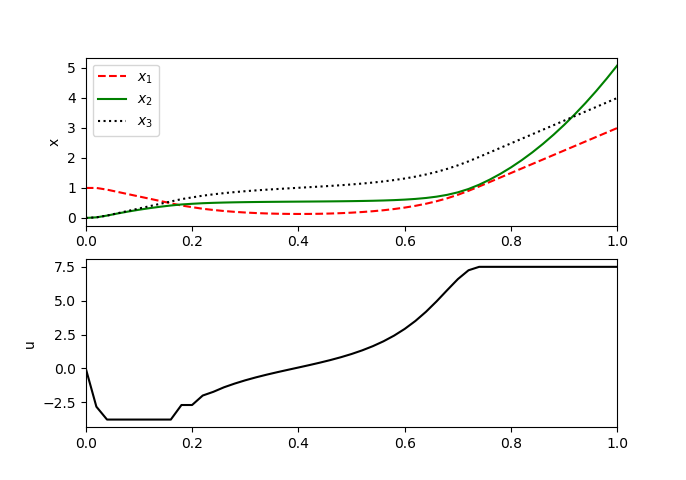
from gekko import GEKKO import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt n = 51 Lp = 4 b = 3 a = 1 m = GEKKO() m.time = np.linspace(0, 1, n) x1 = m.Var(value=a, lb=0, ub=10) x2 = m.Var(value=0, lb=0, ub=10) x3 = m.Var(value=0, lb=0, ub=10) u = m.MV(value=0, lb=-10, ub=20) # integer=True, tmp = np.zeros(n) tmp[-1] = 1 final = m.Param(value=tmp) m.Equation(x1.dt() == u) m.Equation(x2.dt() == x1 * (1+u**2)**0.5) m.Equation(x3.dt() == (1+u**2)**0.5) # m.Equation((x1-b)*final == 0) # m.Equation((x3-Lp)*final == 0) m.Obj(1000*(x1-b)**2*final) m.Obj(1000*(x3-Lp)**2*final) #m.fix(x1, n-1, b) #m.fix(x3, n-1, Lp) m.options.SOLVER = 3 m.options.NODES = 3 m.options.IMODE = 6 m.Obj(x2*final) # initialize m.options.TIME_SHIFT = 0 u.STATUS = 0 m.solve() # solve u.STATUS = 1 u.DCOST = 1e-3 m.solve() plt.subplot(2,1,1) plt.plot(m.time,x1.value,'r--',label=r'$x_1$') plt.plot(m.time,x2.value,'g-',label=r'$x_2$') plt.plot(m.time,x3.value,'k:',label=r'$x_3$') plt.ylabel('x') plt.legend() plt.xlim([0,1]) plt.subplot(2,1,2) plt.plot(2,1,2) plt.plot(m.time,u.value,'k-',label=r'$u$') plt.ylabel('u') plt.xlim([0,1]) plt.show()
Solver Results
An MINLP solution is calculated with IPOPT with an objective function value of 5.13266.