Batch reactor (GEKKO)
From mintOC
This page contains a solution of the Batch reactor problem in GEKKO Python format. The model in Python code for a fixed control discretization grid uses orthogonal collocation and a simultaneous optimization method. The GEKKO package is available with pip install gekko.
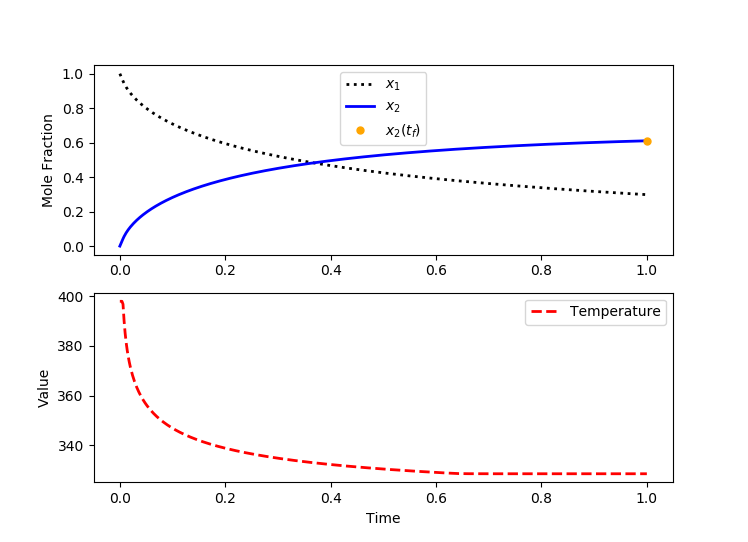
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from gekko import GEKKO m = GEKKO() nt = 501 m.time = np.linspace(0,1,nt) # Variables x1 = m.Var(value=1) x2 = m.Var(value=0) T = m.MV(value=398,lb=298,ub=398) T.STATUS = 1 T.DCOST = 1e-6 k1 = m.Intermediate(4000*m.exp(-2500/T)) k2 = m.Intermediate(6.2e5*m.exp(-5000/T)) p = np.zeros(nt) p[-1] = 1.0 final = m.Param(value=p) # Equations m.Equation(x1.dt()==-k1*x1**2) m.Equation(x2.dt()==k1*x1**2 - k2*x2) # Objective Function # maximize final x2 m.Obj(-x2*final) m.options.IMODE = 6 m.options.NODES = 3 m.solve() print('Optimal x2(tf): ' + str(x2.value[-1])) plt.figure(1) plt.subplot(2,1,1) plt.plot(m.time,x1.value,'k:',\ LineWidth=2,label=r'$x_1$') plt.plot(m.time,x2.value,'b-',\ LineWidth=2,label=r'$x_2$') plt.plot(m.time[-1],x2.value[-1],'o',\ color='orange',MarkerSize=5,\ label=r'$x_2\left(t_f\right)$') plt.legend() plt.ylabel('Mole Fraction') plt.subplot(2,1,2) plt.plot(m.time,T.value,'r--',\ LineWidth=2,label='Temperature') plt.ylabel(r'$T/;(^oC)$') plt.legend(loc='best') plt.xlabel('Time') plt.ylabel('Value') plt.show()
A solution is calculated with an objective function value of x2(tf) = 0.6108.