Category:Boolean variables
Discrete switching events can also be expressed by means of Boolean variables and logical implications. E.g., by introducing logical functions
![\delta_i: [0, t_f] \mapsto \{ \mathrm{true}, \mathrm{false} \}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/1/2/f/12f0eb048533d6e0735023f25291eb9a.png)
that indicate whether a model formulation ![F_i[x,u,v]](https://mintoc.de/images/math/3/0/0/300379516af3af3001dc366fb69a9c28.png) is active at time
is active at time 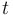 , both state-dependent switches and outer convexification formulations may be written as disjunctive programs, i.e., optimization problems involving Boolean variables and logical conditions. Using disjunctive programs can be seen as a more natural way of modeling discrete events and has the main advantage of resulting in tighter relaxations of the discrete dicisions, when compared to integer programming techniques. More details can be found, e.g., in [Grossmann2002]Author: I.E. Grossmann
, both state-dependent switches and outer convexification formulations may be written as disjunctive programs, i.e., optimization problems involving Boolean variables and logical conditions. Using disjunctive programs can be seen as a more natural way of modeling discrete events and has the main advantage of resulting in tighter relaxations of the discrete dicisions, when compared to integer programming techniques. More details can be found, e.g., in [Grossmann2002]Author: I.E. Grossmann
Journal: Optimization and Engineering
Pages: 227--252
Title: Review of Nonlinear Mixed-Integer and Disjunctive Programming Techniques
Volume: 3
Year: 2002 [Oldenburg2005]Address: D\"usseldorf
[Oldenburg2005]Address: D\"usseldorf
Author: J. Oldenburg
Publisher: VDI Verlag
Series: Fortschritt-Berichte VDI Reihe 3, Verfahrens\-technik
Title: Logic--based modeling and optimization of discrete--continuous dynamic systems
Volume: 830
Year: 2005 [Oldenburg2008]Author: J. Oldenburg; W. Marquardt
[Oldenburg2008]Author: J. Oldenburg; W. Marquardt
Journal: Computers \& Chemical Engineering
Number: 10
Pages: 2346--2364
Title: Disjunctive modeling for optimal control of hybrid systems
Volume: 32
Year: 2008 .
.
References
| [Grossmann2002] | I.E. Grossmann (2002): Review of Nonlinear Mixed-Integer and Disjunctive Programming Techniques. Optimization and Engineering, 3, 227--252 |  |
| [Oldenburg2005] | J. Oldenburg (2005): Logic--based modeling and optimization of discrete--continuous dynamic systems. (%edition%). VDI Verlag, D\"usseldorf, %pages% |  |
| [Oldenburg2008] | J. Oldenburg; W. Marquardt (2008): Disjunctive modeling for optimal control of hybrid systems. Computers \& Chemical Engineering, 32, 2346--2364 |  |
This category currently contains no pages or media.