Double Tank (GEKKO)
From mintOC
This page contains a solution of the Double Tank in GEKKO Python format. The GEKKO package is available with pip install gekko. The Python code uses orthogonal collocation and a simultaneous optimization method. The integral is converted to a differential equation through differentiation and definition of a new variable x3.
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from gekko import GEKKO m = GEKKO() # create GEKKO model # Add 0.01 as first step # 0,0.01,0.1,0.2,0.3,...9.9,10.0) m.time = np.insert(np.linspace(0,10,201),1,0.01) # change solver options m.solver_options = ['minlp_gap_tol 0.001',\ 'minlp_maximum_iterations 10000',\ 'minlp_max_iter_with_int_sol 100',\ 'minlp_branch_method 1',\ 'minlp_integer_tol 0.001',\ 'minlp_integer_leaves 0',\ 'minlp_maximum_iterations 200'] k1 = 2 k2 = 3 last = m.Param(np.zeros(202)) last.value[-1] = 1 sigma=m.MV(value=1,lb=1,ub=2,integer=True) x1 = m.Var(value=2) x2 = m.Var(value=2) x3 = m.Var(value=0) sigma.STATUS = 1 m.Obj(last*x3) m.Equations([x1.dt() == sigma - m.sqrt(x1),\ x2.dt() == m.sqrt(x1) - m.sqrt(x2),\ x3.dt() == k1*(x2-k2)**2]) m.options.IMODE = 6 m.options.NODES = 3 m.options.SOLVER = 1 m.options.MV_TYPE = 0 m.solve() plt.figure(1) plt.step(m.time,sigma.value,'r-',label=r'$\sigma$ (1/2)') plt.plot(m.time,x1.value,'k-',label=r'$x_1$') plt.plot(m.time,x2.value,'g-',label=r'$x_2$') plt.xlabel('Time') plt.ylabel('Variables') plt.legend(loc='best') plt.show()
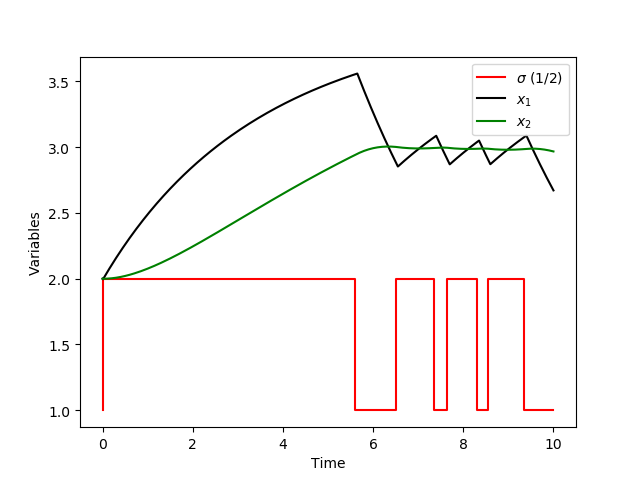
Results with APOPT (MINLP)
An MINLP solution is calculated with APOPT with an objective function value of 4.767757.