Difference between revisions of "Double Tank"
FelixMueller (Talk | contribs) |
FelixMueller (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | The double tank problem is a basic example for a switching system. It contains the dynamics of an upper and a lower tank, connected to each other with a pipe. The goal is to minimize the deviation of a certain fluid level <math>k_2</math> in the lower tank. The problem was introduced and discussed in a variety of publications for the optimal control of constrained switched systems, e.g. | + | The double tank problem is a basic example for a switching system. It contains the dynamics of an upper and a lower tank, connected to each other with a pipe. The goal is to minimize the deviation of a certain fluid level <math>k_2</math> in the lower tank. The problem was introduced and discussed in a variety of publications for the optimal control of constrained switched systems, e.g. <bib id="Henrion2014" /> (Link: [http://homepages.laas.fr/henrion/papers/switch.pdf Henrion et al.]) and <bib id="Vasudevan2013" /> (Link: [http://epubs.siam.org/doi/pdf/10.1137/120901507 Vasudevan et al.]). |
== Mathematical formulation == | == Mathematical formulation == | ||
Revision as of 19:37, 3 March 2016
| Double Tank | |
|---|---|
| State dimension: | 1 |
| Differential states: | 2 |
| Discrete control functions: | 1 |
| Interior point equalities: | 2 |
The double tank problem is a basic example for a switching system. It contains the dynamics of an upper and a lower tank, connected to each other with a pipe. The goal is to minimize the deviation of a certain fluid level 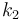 in the lower tank. The problem was introduced and discussed in a variety of publications for the optimal control of constrained switched systems, e.g. [Henrion2014]The entry doesn't exist yet. (Link: Henrion et al.) and [Vasudevan2013]The entry doesn't exist yet. (Link: Vasudevan et al.).
in the lower tank. The problem was introduced and discussed in a variety of publications for the optimal control of constrained switched systems, e.g. [Henrion2014]The entry doesn't exist yet. (Link: Henrion et al.) and [Vasudevan2013]The entry doesn't exist yet. (Link: Vasudevan et al.).
Contents
[hide]Mathematical formulation
![\begin{array}{llll}
\displaystyle \min_{\sigma} & \displaystyle \int_{0}^{T} & k_1(x_2-k_2)^2 \; \text{d}t\\[1.5ex]
\mbox{s.t.} & \dot{x}_1 & = c_{\sigma(t)}-\sqrt{x_1}, \\[1.5ex]
& \dot{x}_2 & = \sqrt{x_1}-\sqrt{x_2}, \\[1.5ex]
& x(0) & = (2,2)^T, \\[1.5ex]
& \sigma(t) & \in \{1,2\} \qquad &\text{for } t\in[0,T].\\[1.5ex]
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/e/5/1/e510dbcc83fc45b2984d452d9298c738.png)
The two states of the system correspond to the fluid levels of an upper and a lower tank.
The output of the upper tank flows into the lower tank, the output of the lower
tank exits the system, and the flow into the upper tank is restricted to either 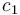 [lt/s]
or
[lt/s]
or 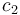 [lt/s]. The dynamics in each mode are then derived using Torricelli’s law, as
shown in constraints 1 and 2. The objective of the optimization is to have the fluid level in the
lower tank equal to
[lt/s]. The dynamics in each mode are then derived using Torricelli’s law, as
shown in constraints 1 and 2. The objective of the optimization is to have the fluid level in the
lower tank equal to 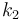 [m], as reflected in the cost function.
[m], as reflected in the cost function.
Parameters
In an exemplary test, the parameters were chosen to be:
| Symbol | Value |
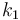
|
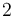
|
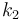
|
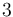
|
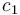
|
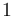
|
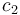
|
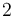
|
|
|
Reference Solution
The problem was solved in Matlab (version 2014b) with Switch. The switch codes rely on GloptiPoly 3 and the solver SeDuMi 1.3 (optimization over symmetric cones).
By introducing the lifts 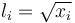 , algebraically constrained as
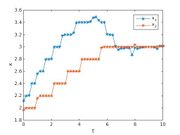
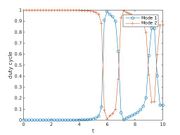
, algebraically constrained as 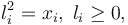 the problem is recast with polynomial data. In this way way switch in connection with GloptiPoly3 can be applied. GloptiPoly 3 is a Matlab package developed by Didier Henrion for generalized problems of moments and needs polynomial input data. The exact code used to solve the problem can be found under Double Tank (switch). The calculated objective is 4.7296 with the following trajectories of states and controls:
the problem is recast with polynomial data. In this way way switch in connection with GloptiPoly3 can be applied. GloptiPoly 3 is a Matlab package developed by Didier Henrion for generalized problems of moments and needs polynomial input data. The exact code used to solve the problem can be found under Double Tank (switch). The calculated objective is 4.7296 with the following trajectories of states and controls:
- Reference solution plots
Source Code
Model descriptions are available in
References
There were no citations found in the article.
CLAEYS, Mathieu; DAAFOUZ Jamal; HENRION Didier Modal occupation measures and LMI relaxations for nonlinear switched systems control. arXiv preprint arXiv:1404.4699 (2014)
VASUDEVAN, Ramanarayan, et al. Consistent Approximations for the Optimal Control of Constrained Switched Systems---Part 2: An Implementable Algorithm. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2013, 51. Jg., Nr. 6, S. 4484-4503.