Difference between revisions of "Fuller's initial value multimode problem"
From mintOC
ClemensZeile (Talk | contribs) |
ClemensZeile (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
}}<!-- Do not insert line break here or Dimensions Box moves up in the layout... | }}<!-- Do not insert line break here or Dimensions Box moves up in the layout... | ||
| − | -->This site describes a Fuller's problem variant with no terminal constraints and additional Mayer term for penalizing deviation from given reference values. | + | -->This site describes a Fuller's problem variant with no terminal constraints and additional Mayer term for penalizing deviation from given reference values. Furthermore, this variant comprises four binary controls instead of only one control. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | Furthermore, this variant comprises four binary controls instead of only one control. | + | |
== Mathematical formulation == | == Mathematical formulation == | ||
Latest revision as of 23:56, 8 January 2018
| Fuller's initial value multimode problem | |
|---|---|
| State dimension: | 1 |
| Differential states: | 2 |
| Discrete control functions: | 4 |
| Interior point equalities: | 2 |
This site describes a Fuller's problem variant with no terminal constraints and additional Mayer term for penalizing deviation from given reference values. Furthermore, this variant comprises four binary controls instead of only one control.
Mathematical formulation
For ![t \in [t_0, t_f]](https://mintoc.de/images/math/5/5/8/55823791d9100bcb5461801aff4f6edd.png) almost everywhere the mixed-integer optimal control problem is given by
almost everywhere the mixed-integer optimal control problem is given by
![\begin{array}{llcl}
\displaystyle \min_{x, w} & \int_{t_0}^{t_f} x_0^2 & \; \mathrm{d} t & + (x(t_f)-x_T)^2 \\[1.5ex]
\mbox{s.t.} & \dot{x}_0 & = & x_1+ \sum\limits_{i=1}^{4} c_{0,i} \omega_i, \\
& \dot{x}_1 & = & 1 + \sum\limits_{i=1}^{4} c_{1,i} \omega_i, \\[1.5ex]
& 1 &=& \sum\limits_{i=1}^{4}w_i(t), \\
& x(0) &=& x_S, \\
& w(t) &\in& \{0, 1\}.
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/1/9/c/19cd2b7156ddbe83f4ad2b666cead397.png)
Parameters
We use 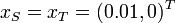 together with:
together with:
![\begin{array}{rcl}
[t_0, t_f] &=& [0, 1],\\
(c_{0,1}, c_{1,1}) &=& (0, -2),\\
(c_{0,2}, c_{1,2}) &=& (0, -0.5),\\
(c_{0,3}, c_{1,3}) &=& (0, -3),\\
(c_{0,4}, c_{1,4}) &=& (0, 0).
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/7/f/2/7f2a2b8ecd6fa85d2e48098cf5349e4d.png)
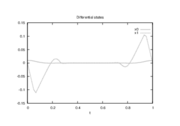
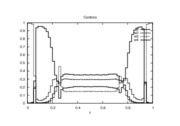
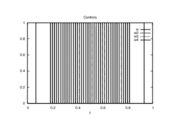
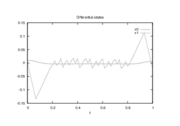
Reference Solutions
If the problem is relaxed, i.e., we demand that 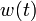 be in the continuous interval
be in the continuous interval ![[0, 1]](https://mintoc.de/images/math/c/c/f/ccfcd347d0bf65dc77afe01a3306a96b.png) instead of the binary choice
instead of the binary choice 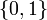 , the optimal solution can be determined by means of direct optimal control.
, the optimal solution can be determined by means of direct optimal control.
The optimal objective value of the relaxed problem with 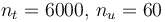 is
is 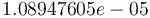 . The objective value of the binary controls obtained by Combinatorial Integral Approimation (CIA) is
. The objective value of the binary controls obtained by Combinatorial Integral Approimation (CIA) is 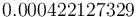 .
.
- Reference solution plots