Catalyst mixing problem
From mintOC
Revision as of 21:15, 12 January 2018 by ClemensZeile (Talk | contribs)
| Catalyst mixing problem | |
|---|---|
| State dimension: | 1 |
| Differential states: | 2 |
| Continuous control functions: | 1 |
| Path constraints: | 2 |
| Interior point equalities: | 2 |
The Catalyst mixing problem seeks an optimal policy for mixing two catalysts "along the length of a tubular plug ow reactor involving several reactions". (Cite and problem taken from the COPS library)
Mathematical formulation
The problem is given by
![\begin{array}{llcl}
\displaystyle \min_{x, w} &-1 + x_1(t_f) + x_2(t_f) \\[1.5ex]
\mbox{s.t.}
& \dot{x}_1 & = & w(t) ( 10 x_2(t) - x_1(t)), \\
& \dot{x}_2 & = & w(t) ( x_1(t) - 10 x_2(t)) - (1 - w(t)) \, x_2(t) , \\
& x(t_0) &=& (1, 0)^T, \\
& w(t) &\in& \{0,1\}.
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/d/5/3/d53aa67777e79cc7de1b69839aa12945.png)
Parameters
In this model the parameters used are 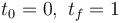 .
.
Reference Solution
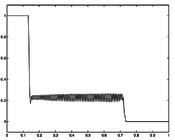
If the problem is relaxed, i.e., we demand that w(t) be in the continuous interval [0, 1] instead of the binary choice \{0,1\}, the optimal solution can be determined by means of direct optimal control.
- Reference solution plots
Results with relaxed controls and collocation from the COPS library
Source Code
Model descriptions are available in