Gravity Turn Maneuver (Casadi)
From mintOC
Revision as of 14:09, 13 December 2015 by MirkoHahn (Talk | contribs) (Corrected due to error in derivative of angle to vertical; added comments and intermediate expressions)
This page contains a discretized version of the OCP Gravity Turn Maneuver in CasADi 2.4.2 format. The continuous model was discretized using a direct multiple shooting approach with 300 shooting nodes distributed equidistantly over a variable time horizon. The control grid is equal to the DMS grid. An initial solution is chosen by linearly interpolating between initial and terminal state.
CasADi
# ---------------------------------------------------------------- # Gravity Turn Maneuver with direct multiple shooting using CVodes # (c) Mirko Hahn # ---------------------------------------------------------------- from casadi import * # Artificial model parameters N = 300 # Number of shooting intervals vel_eps = 1e-6 # Initial velocity (km/s) # Vehicle parameters m0 = 11.3 # Launch mass (t) m1 = 1.3 # Dry mass (t) g0 = 9.81e-3 # Gravitational acceleration at altitude zero (km/s^2) r0 = 6.0e2 # Radius at altitude zero (km) Isp = 300.0 # Specific impulse (s) Fmax = 600.0e-3 # Maximum thrust (MN) # Atmospheric parameters cd = 0.021 # Drag coefficients A = 1.0 # Reference area (m^2) H = 5.6 # Scale height (km) rho = (1.0 * 1.2230948554874) # Density at altitude zero # Target orbit parameters h_obj = 75 # Target altitude (km) v_obj = 2.287 # Target velocity (km/s) q_obj = 0.5 * pi # Target angle to vertical (rad) # Create symbolic variables x = SX.sym('[m, v, q, h, d]') # Vehicle state u = SX.sym('u') # Vehicle controls T = SX.sym('T') # Time horizon (s) # Introduce symbolic expressions for important composite terms Fthrust = Fmax * u Fdrag = 0.5e3 * A * cd * rho * exp(-x[3] / H) * x[1]**2 r = x[3] + r0 g = g0 * (r0 / r)**2 vhor = x[1] * sin(x[2]) vver = x[1] * cos(x[2]) # Build symbolic expressions for ODE right hand side mdot = -(Fmax / (Isp * g0)) * u vdot = (Fthrust - Fdrag) / x[0] - g * cos(x[2]) hdot = vver ddot = vhor / r qdot = g * sin(x[2]) / x[1] - ddot # Build the DAE function ode = [ mdot, vdot, qdot, hdot, ddot ] quad = u dae = SXFunction("dae", daeIn(x=x, p=vertcat([u, T])), daeOut(ode=T*vertcat(ode), quad=T*quad)) I = Integrator("I", "cvodes", dae, {'t0': 0.0, 'tf': 1.0 / N}) # Specify upper and lower bounds as well as initial values for DAE parameters, # states and controls p_min = [120.0] p_max = [600.0] p_init = [120.0] u_min = [0.0] u_max = [1.0] u_init = [0.5] x0_min = [m0, vel_eps, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] x0_max = [m0, vel_eps, 0.5 * pi, 0.0, 0.0] x0_init = [m0, vel_eps, 0.05 * pi, 0.0, 0.0] xf_min = [m1, v_obj, q_obj, h_obj, 0.0] xf_max = [m0, v_obj, q_obj, h_obj, inf] xf_init = [m1, v_obj, q_obj, h_obj, 0.0] x_min = [m1, vel_eps, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] x_max = [m0, inf, pi, inf, inf] x_init = [0.5 * (m0 + m1), 0.5 * v_obj, 0.5 * q_obj, 0.5 * h_obj, 0.0] # Useful variable block sizes np = 1 # Number of parameters nx = x.size1() # Number of states nu = u.size1() # Number of controls ns = nx + nu # Number of variables per shooting interval # Introduce symbolic variables and disassemble them into blocks V = MX.sym('X', N * ns + nx + np) P = V[0] X = [V[np+i*ns:np+i*ns+nx] for i in range(0, N+1)] U = [V[np+i*ns+nx:np+(i+1)*ns] for i in range(0, N)] # Nonlinear constraints and Lagrange objective G = [] F = 0.0 # Build DMS structure x0 = p_init + x0_init for i in range(0, N): Y = I({'x0': X[i], 'p': vertcat([U[i], P])}) G = G + [Y['xf'] - X[i+1]] F = F + Y['qf'] frac = float(i+1) / N x0 = x0 + u_init + [x0_init[i] + frac * (xf_init[i] - x0_init[i]) for i in range(0, nx)] # Lower and upper bounds for solver lbg = 0.0 ubg = 0.0 lbx = p_min + x0_min + u_min + (N-1) * (x_min + u_min) + xf_min ubx = p_max + x0_max + u_max + (N-1) * (x_max + u_max) + xf_max # Solve the problem using IPOPT nlp = MXFunction("nlp", nlpIn(x=V), nlpOut(f=m0 - X[-1][0], g=vertcat(G))) S = NlpSolver("S", "ipopt", nlp, {'tol': 1e-5}) r = S({ 'x0' : x0, 'lbx': lbx, 'ubx': ubx, 'lbg': lbg, 'ubg': ubg }) # Extract state sequences and parameters from result x = r['x'] f = r['f'] T = x[0] t = [i * (T / N) for i in range(0, N+1)] m = x[np ::ns].get() v = x[np+1::ns].get() q = x[np+2::ns].get() h = x[np+3::ns].get() d = x[np+4::ns].get() u = x[np+nx::ns].get() + [0.0]
Results
The solution is calculated using IPOPT (3.11.9, default settings with tolerance 1e-5, using linear solver MUMPS in sequential mode on Ubuntu 15.10 for x86-64 with Linux 4.2.0-19-generic, Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-4790K CPU @ 4.00GHz, 16 GB RAM). The objective function value is 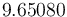 . IPOPT finds the solution in 84 iterations (77.466 seconds proc time).
. IPOPT finds the solution in 84 iterations (77.466 seconds proc time).