Difference between revisions of "Car testdrive (elliptic track)"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
Four controls represent the driver's choice on steering and velocity. We denote with <math>w_\delta</math> the steering wheel's angular velocity. The force <math>F_\text{B}</math> controls the total braking force, while the accelerator pedal position <math>\phi</math> is translated into an accelerating force. Finally, the selected gear <math>\mu</math> influences the effective engine torque's transmission. | Four controls represent the driver's choice on steering and velocity. We denote with <math>w_\delta</math> the steering wheel's angular velocity. The force <math>F_\text{B}</math> controls the total braking force, while the accelerator pedal position <math>\phi</math> is translated into an accelerating force. Finally, the selected gear <math>\mu</math> influences the effective engine torque's transmission. | ||
| + | == Resulting MIOCP == | ||
| + | |||
| + | For <math>t \in [t_0, t_f]</math> almost everywhere the mixed-integer optimal control problem is given by | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \begin{array}{llcl} | ||
| + | \displaystyle \min_{x(\cdot), u(\cdot), \mu(\cdot)} & t_\text{f} \\[1.5ex] | ||
| + | \mbox{s.t.} & \dot{x}(t) & = & f(t, x(t), u(t), \mu(t)), \\ | ||
| + | & x(t_0) &=& x_0, \\ | ||
| + | & r(t,x(t),u(t)) &\geq& 0, \\ | ||
| + | & \mu(t) &\in& \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5\}. | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Source Code == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Variants == | ||
| + | |||
| + | See testdrive [[Car testdrive | overview page]]. | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<bibreferences/> | <bibreferences/> | ||
Revision as of 15:00, 25 November 2008
| Car testdrive (elliptic track) | |
|---|---|
| State dimension: | 1 |
| Differential states: | 7 |
| Continuous control functions: | 3 |
| Discrete control functions: | 1 |
| Interior point inequalities: | 7 |
The elliptic track testdrive problem is a time optimal periodic control problem with gear shift, first introduced in <bibref>Sager2009a</bibref>.
Mathematical formulation
The mathematical equations form a small-scale ODE model.
The vehicle dynamics are based on a single-track model, derived under the simplifying assumption that rolling and pitching of the car body can be neglected. Consequentially, only a single front and rear wheel is modeled, located in the virtual center of the original two wheels. Motion of the car body is considered on the horizontal plane only.
Four controls represent the driver's choice on steering and velocity. We denote with 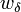 the steering wheel's angular velocity. The force
the steering wheel's angular velocity. The force 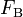 controls the total braking force, while the accelerator pedal position
controls the total braking force, while the accelerator pedal position 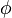 is translated into an accelerating force. Finally, the selected gear
is translated into an accelerating force. Finally, the selected gear 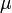 influences the effective engine torque's transmission.
influences the effective engine torque's transmission.
Resulting MIOCP
For ![t \in [t_0, t_f]](https://mintoc.de/images/math/5/5/8/55823791d9100bcb5461801aff4f6edd.png) almost everywhere the mixed-integer optimal control problem is given by
almost everywhere the mixed-integer optimal control problem is given by
![\begin{array}{llcl}
\displaystyle \min_{x(\cdot), u(\cdot), \mu(\cdot)} & t_\text{f} \\[1.5ex]
\mbox{s.t.} & \dot{x}(t) & = & f(t, x(t), u(t), \mu(t)), \\
& x(t_0) &=& x_0, \\
& r(t,x(t),u(t)) &\geq& 0, \\
& \mu(t) &\in& \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5\}.
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/0/0/3/00382d7408dddcf936f8d70afb496034.png)
Source Code
Variants
See testdrive overview page.
References
<bibreferences/>