Difference between revisions of "F-8 aircraft"
m (Corrected errors in formula) |
m (Added reference solution section) |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
== Reference solutions == | == Reference solutions == | ||
| − | + | We provide here a comparison of different solutions reported in the literature. The numbers show the respective lengths <math>t_i - t_{i-1}</math> of the switching arcs with the value of <math>w(t)</math> on the upper or lower bound (given in the second column). ''Claim'' denotes what is stated in the respective publication, ''Simulation'' shows values obtained by a simulation with a Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg method of 4th/5th order and an integration tolerance of <math>10^{-8}</math>. | |
| − | + | {| border=1 | |
| − | + | |- bgcolor=grey | |
| − | + | ! Arc !! w(t) !! Lee et al.<bibref>Lee1997a</bibref> !! Kaya<bibref>Kaya2003</bibref> !! Sager<bibref>Sager2005</bibref> | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | align=center | 1 || align=center | 1 || 0.00000 || 0.10292 || 0.10235 | |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | | align=center | 2 || align=center | 0 || 2.18000 || 1.92793 || 1.92812 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align=center | 3 || align=center | 1 || 0.16400 || 0.16687 || 0.16645 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align=center | 4 || align=center | 0 || 2.88100 || 2.74338 || 2.73071 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align=center | 5 || align=center | 1 || 0.33000 || 0.32992 || 0.32994 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align=center | 6 || align=center | 0 || 0.47200 || 0.47116 || 0.47107 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Claim: Infeasibility || align=center | - || 1.00E-10 || 7.30E-06 || 5.90E-06 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Claim: Objective || align=center | - || 6.035 || 5.74217 || 5.72864 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Simulation: Infeasibility''' || align=center | - || 1.75E-03 || 1.64E-03 || 5.90E-06 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Simulation: Objective''' || align=center | - || 6.035 || 5.74218 || 5.72864 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
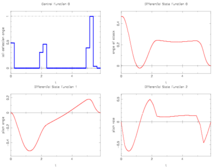
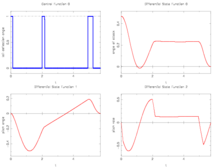
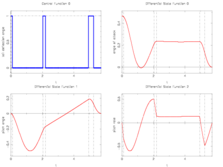
| + | The best known optimal objective value of this problem given is given in Sager 2005<bibref>Sager2005</bibref> by <math>T = 5.72864</math>. The corresponding solution is shown in the rightmost plot. The solution of bang-bang type switches five times, starting with <math>w(t) = 1</math>. | ||
<gallery caption="Reference solution plots" widths="240px" heights="167px" perrow="3"> | <gallery caption="Reference solution plots" widths="240px" heights="167px" perrow="3"> | ||
Revision as of 14:16, 9 November 2008
| F-8 aircraft | |
|---|---|
| State dimension: | 1 |
| Differential states: | 3 |
| Discrete control functions: | 1 |
| Interior point equalities: | 6 |
The F-8 aircraft control problem is based on a very simple aircraft model. The control problem was introduced by Kaya and Noakes in 2003<bibref>Kaya2003</bibref> and aims at controlling an aircraft in a time-optimal way from an initial state to a terminal state.
The mathematical equations form a small-scale ODE Model. The interior point equality conditions fix both initial and terminal values of the differential states.
The optimal integer control functions shows bang bang behavior. The problem is furthermore interesting as it should be reformulated equivalently.
Contents
Mathematical formulation
For ![t \in [0, T]](https://mintoc.de/images/math/e/6/6/e66a2b7fedcba80ccb192b87440f8d9c.png) almost everywhere the mixed-integer optimal control problem is given by
almost everywhere the mixed-integer optimal control problem is given by
![\begin{array}{llcl}
\displaystyle \min_{x, w, T} & T \\[1.5ex]
\mbox{s.t.} & \dot{x}_0 &=& -0.877 \; x_0 + x_2 - 0.088 \; x_0 \; x_2 + 0.47 \; x_0^2 - 0.019 \; x_1^2 - x_0^2 \; x_2 + 3.846 \; x_0^3 \\
&&& - 0.215 \; w + 0.28 \; x_0^2 \; w + 0.47 \; x_0 \; w^2 + 0.63 \; w^3 \\
& \dot{x}_1 &=& x_2 \\
& \dot{x}_2 &=& -4.208 \; x_0 - 0.396 \; x_2 - 0.47 \; x_0^2 - 3.564 \; x_0^3 \\
&&& - 20.967 \; w + 6.265 \; x_0^2 \; w + 46 \; x_0 \; w^2 + 61.4 \; w^3 \\
& x(0) &=& (0.4655,0,0)^T, \\
& x(T) &=& (0,0,0)^T, \\
& w(t) &\in& \{-0.05236,0.05236\}.
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/d/2/b/d2bd7e6d1cc8affb72d59248a105d528.png)
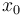 is the angle of attack in radians,
is the angle of attack in radians, 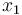 is the pitch angle,
is the pitch angle, 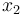 is the pitch rate in rad/s, and the control function
is the pitch rate in rad/s, and the control function 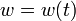 is the tail deflection angle in radians. This model goes back to Garrard<bibref>Garrard1977</bibref>.
is the tail deflection angle in radians. This model goes back to Garrard<bibref>Garrard1977</bibref>.
In the control problem, both initial as terminal values of the differential states are fixed.
Reformulation
The control w(t) is restricted to take values from a finite set only. Hence, the control problem can be reformulated equivalently to
![\begin{array}{llcl}
\displaystyle \min_{x, w, T} & T \\[1.5ex]
\mbox{s.t.} & \dot{x}_0 &=& -0.877 \; x_0 + x_2 - 0.088 \; x_0 \; x_2 + 0.47 \; x_0^2 - 0.019 \; x_1^2 - x_0^2 \; x_2 + 3.846 \; x_0^3 \\
&&& - \left( 0.215 \; \xi - 0.28 \; x_0^2 \; \xi - 0.47 \; x_0 \; \xi^2 - 0.63 \; \xi^3 \right) \; w \\
&&& - \left( - 0.215 \; \xi + 0.28 \; x_0^2 \; \xi + 0.47 \; x_0 \; \xi^2 + 0.63 \; \xi^3 \right) \; (1 - w) \\
& \dot{x}_1 &=& x_2 \\
& \dot{x}_2 &=& -4.208 \; x_0 - 0.396 \; x_2 - 0.47 \; x_0^2 - 3.564 \; x_0^3 \\
&&& - \left( 20.967 \; \xi - 6.265 \; x_0^2 \; \xi -46 \; x_0 \; \xi^2 - 61.4 \; \xi^3 \right) \; w \\
&&& - \left( - 20.967 \; \xi + 6.265 \; x_0^2 \; \xi +46 \; x_0 \; \xi^2 + 61.4 \; \xi^3 \right) \; (1 - w) \\
& x(0) &=& (0.4655,0,0)^T, \\
& x(T) &=& (0,0,0)^T, \\
& w(t) &\in& \{0,1\},
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/9/4/8/948bc48520ff7479903c1e3fcfb545b0.png)
with 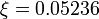 . Note that there is a bijection between optimal solutions of the two problems.
. Note that there is a bijection between optimal solutions of the two problems.
Reference solutions
We provide here a comparison of different solutions reported in the literature. The numbers show the respective lengths 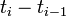 of the switching arcs with the value of
of the switching arcs with the value of 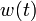 on the upper or lower bound (given in the second column). Claim denotes what is stated in the respective publication, Simulation shows values obtained by a simulation with a Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg method of 4th/5th order and an integration tolerance of
on the upper or lower bound (given in the second column). Claim denotes what is stated in the respective publication, Simulation shows values obtained by a simulation with a Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg method of 4th/5th order and an integration tolerance of 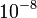 .
.
| Arc | w(t) | Lee et al.<bibref>Lee1997a</bibref> | Kaya<bibref>Kaya2003</bibref> | Sager<bibref>Sager2005</bibref> |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0.00000 | 0.10292 | 0.10235 |
| 2 | 0 | 2.18000 | 1.92793 | 1.92812 |
| 3 | 1 | 0.16400 | 0.16687 | 0.16645 |
| 4 | 0 | 2.88100 | 2.74338 | 2.73071 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.33000 | 0.32992 | 0.32994 |
| 6 | 0 | 0.47200 | 0.47116 | 0.47107 |
| Claim: Infeasibility | - | 1.00E-10 | 7.30E-06 | 5.90E-06 |
| Claim: Objective | - | 6.035 | 5.74217 | 5.72864 |
| Simulation: Infeasibility | - | 1.75E-03 | 1.64E-03 | 5.90E-06 |
| Simulation: Objective | - | 6.035 | 5.74218 | 5.72864 |
The best known optimal objective value of this problem given is given in Sager 2005<bibref>Sager2005</bibref> by 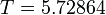 . The corresponding solution is shown in the rightmost plot. The solution of bang-bang type switches five times, starting with
. The corresponding solution is shown in the rightmost plot. The solution of bang-bang type switches five times, starting with 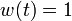 .
.
- Reference solution plots
Source Code
C
The differential equations in C code:
double x1 = xd[0]; double x2 = xd[1]; double x3 = xd[2]; double u0 = -0.05236; double u1 = 0.05236; double f00, f10, f20; double f01, f11, f21; f00 = - 0.877*x1 + x3 - 0.088*x1*x3 + 0.47*x1*x1 - 0.019*x2*x2 - x1*x1*x3 + 3.846*x1*x1*x1 - 0.215*u0 + 0.28*x1*x1*u0 + 0.47*x1*u0*u0 + 0.63*u0*u0*u0; f10 = x3; f20 = - 4.208*x1 - 0.396*x3 - 0.47*x1*x1 - 3.564*x1*x1*x1 - 20.967*u0 + 6.265*x1*x1*u0 + 46*x1*u0*u0 + 61.4*u0*u0*u0; f01 = - 0.877*x1 + x3 - 0.088*x1*x3 + 0.47*x1*x1 - 0.019*x2*x2 - x1*x1*x3 + 3.846*x1*x1*x1 - 0.215*u1 + 0.28*x1*x1*u1 + 0.47*x1*u1*u1 + 0.63*u1*u1*u1; f11 = x3; f21 = - 4.208*x1 - 0.396*x3 - 0.47*x1*x1 - 3.564*x1*x1*x1 -20.967*u1 + 6.265*x1*x1*u1 + 46*x1*u1*u1 + 61.4*u1*u1*u1; rhs[0] = u[0]*f01 + (1-u[0])*f00; rhs[1] = u[0]*f11 + (1-u[0])*f10; rhs[2] = u[0]*f21 + (1-u[0])*f20;
Miscellaneous and Further Reading
See <bibref>Kaya2003</bibref> and <bibref>Sager2005</bibref> for details.
References
<bibreferences/>