Robot arm problem
| Robot arm problem | |
|---|---|
| State dimension: | 1 |
| Differential states: | 3 |
| Continuous control functions: | 3 |
| Path constraints: | 12 |
| Interior point equalities: | 12 |
The robot arm problem focuses on minimizing the time used by a robot arm to move from an origin to a destination.
The arm is a bar of length 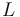 and sticks out distance
and sticks out distance 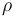 from its moving axis, while sticking out distance
from its moving axis, while sticking out distance 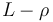 in the other direction. The problem can be found in [Moessner1995]Address: Im Neuenheimer Feld 368, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany
in the other direction. The problem can be found in [Moessner1995]Address: Im Neuenheimer Feld 368, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany
Author: M. Moessner-Beigel
Month: November
School: Ruprecht-Karls-Universit\"at Heidelberg
Title: Optimale Steuerung f\"ur Industrieroboter unter Ber\"ucksichtigung der getriebebedingten Elastizit\"at
Type: Diplomarbeit
Year: 1995 or in the COPS library.
or in the COPS library.
Model formulation
The problem is set up using the length 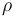 , "the vertical angles
, "the vertical angles 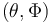 from the horizontal plane, the controls
from the horizontal plane, the controls 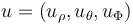 and the final time
and the final time 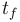 ".
".
The moving robot is modelled with the following equations:
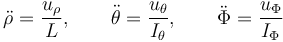
where 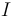 characterizes the moment of inertia, i.e.
characterizes the moment of inertia, i.e.
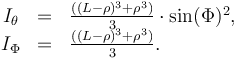
The path constraints on the states 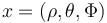 and on the controls
and on the controls 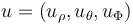 as well as the boundary conditions can be seen in the optimization problem further down.
as well as the boundary conditions can be seen in the optimization problem further down.
Optimization problem
![\begin{array}{llclr}
\displaystyle \min_{x, u, t_f} & t_f \\[1.5ex]
\mbox{s.t.}
& \ddot{\rho} & = & \frac{u_{\rho}}{L}, \\
& \ddot{\theta} & = & \frac{u_{\theta}}{I_{\theta}}, \\
& \ddot{\Phi} & = & \frac{u_{\Phi}}{I_{\Phi}}, \\[1.5ex]
& x(0) &=& (4.5, 0, \frac{\pi}{4})^T, \\
& x(t_f) &=& (4.5, \frac{2\pi}{3}, \frac{\pi}{4})^T, \\
& \dot{x}(0) &=& (0,0,0)^T, \\
& \dot{x}(t_f) &=& (0,0,0)^T, \\[1.5ex]
& \rho(t) & \in & [0,L],\\
& \theta(t) & \in & [-\pi, \pi],\\
& \Phi(t) & \in & [0, \pi],\\
& u_{\rho} & \leq & 1,\\
& u_{\theta} & \leq & 1,\\
& u_{\Phi} & \leq & 1.\\
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/7/9/4/794ce58a20a64c69782ed42693cfd9a1.png)
where 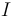 is the moment of inertia as above.
is the moment of inertia as above.
Source Code
Model descriptions are available in
== References ==
| [Moessner1995] | M. Moessner-Beigel: Optimale Steuerung f\"ur Industrieroboter unter Ber\"ucksichtigung der getriebebedingten Elastizit\"at, 1995 |  |