Difference between revisions of "Goddart's rocket problem"
From mintOC
FelixMueller (Talk | contribs) |
FelixMueller (Talk | contribs) (→Mathematical formulation) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|nd = 1 | |nd = 1 | ||
|nx = 3 | |nx = 3 | ||
| − | | | + | |nu = 1 |
| − | |nre = | + | |nc = 1 |
| + | |nre = 4 | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 25: | Line 26: | ||
\begin{array}{llcll} | \begin{array}{llcll} | ||
\displaystyle \min_{m,r,v,u,T} & -m(T)\\[1.5ex] | \displaystyle \min_{m,r,v,u,T} & -m(T)\\[1.5ex] | ||
| − | \mbox{s.t.} & \dot{r} | + | \mbox{s.t.} & \dot{r} & = & v, \\ |
| − | & \dot{v} | + | & \dot{v} & = & -\frac{1}{r^2} + \frac{1}{m} (T_{max}u-D(r,v)) \\[1.5ex] |
| − | & \dot{m} | + | & \dot{m} & = & -b T_{max} u, \\ |
& u(t) &\in& [0,1] \\ | & u(t) &\in& [0,1] \\ | ||
& r(0) &=& r_0, \\ | & r(0) &=& r_0, \\ | ||
| Line 33: | Line 34: | ||
& m(0) &=& m_0, \\ | & m(0) &=& m_0, \\ | ||
& r(T) &=& r_T, \\ | & r(T) &=& r_T, \\ | ||
| − | & D(r | + | & D(r,v)&\le& C \\ |
& T \, free | & T \, free | ||
\end{array} | \end{array} | ||
| Line 73: | Line 74: | ||
* [[:Category: Bocop | Bocop code]] at [[Goddart's rocket problem (Bocop)]] | * [[:Category: Bocop | Bocop code]] at [[Goddart's rocket problem (Bocop)]] | ||
| − | + | * [[:Category: AMPL/TACO | AMPL/TACO code]] at [[Goddart's rocket problem (TACO)]] | |
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 17:08, 22 February 2016
| Goddart's rocket problem | |
|---|---|
| State dimension: | 1 |
| Differential states: | 3 |
| Continuous control functions: | 1 |
| Path constraints: | 1 |
| Interior point equalities: | 4 |
In Goddart's rocket problem we model the ascent (vertical; restricted to 1 dimension) of a rocket. The aim is to reach a certain altitude with minimal fuel consumption. It is equivalent to maximize the mass at the final altitude.
Contents
Variables
The state variables 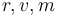 describe the altitude(radius), speed and mass respectively.
describe the altitude(radius), speed and mass respectively.
The drag is given by
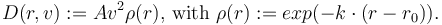
Mathematical formulation
![\begin{array}{llcll}
\displaystyle \min_{m,r,v,u,T} & -m(T)\\[1.5ex]
\mbox{s.t.} & \dot{r} & = & v, \\
& \dot{v} & = & -\frac{1}{r^2} + \frac{1}{m} (T_{max}u-D(r,v)) \\[1.5ex]
& \dot{m} & = & -b T_{max} u, \\
& u(t) &\in& [0,1] \\
& r(0) &=& r_0, \\
& v(0) &=& v_0, \\
& m(0) &=& m_0, \\
& r(T) &=& r_T, \\
& D(r,v)&\le& C \\
& T \, free
\end{array}](https://mintoc.de/images/math/1/5/1/1510d912f548b873254257dbd8da014e.png)
Parameters
Reference Solution
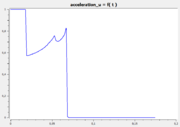
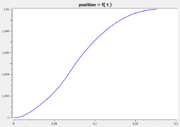
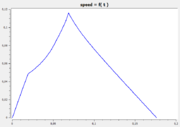
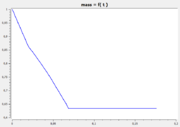
The following reference solution was generated using BOCOP. The optimal value of the objective function is -0.63389.
- Reference solution plots
Source Code
Model descriptions are available in:
References
The Problem can be found in the BOCOP User Guide.