Difference between revisions of "Oil shale pyrolysis (GEKKO)"
From mintOC
(Oil shale pyrolysis solution in GEKKO) |
|||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | A solution is calculated with an objective function value of <math>x_2(t_f) = | + | A solution is calculated with an objective function value of <math>x_2(t_f) = 0.35062</math>. |
[[File:Oil_Shale_Pyrolysis_GEKKO.png]] | [[File:Oil_Shale_Pyrolysis_GEKKO.png]] | ||
[[Category:Gekko]] | [[Category:Gekko]] | ||
Revision as of 03:04, 15 March 2019
This page contains a solution of the Oil Shale Pyrolysis problem in GEKKO Python format. The model in Python code for a fixed control discretization grid uses orthogonal collocation and a simultaneous optimization method. The GEKKO package is available with pip install gekko.
from gekko import GEKKO import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt m=GEKKO() nt = 101 m.time = np.linspace(0,1,nt) # Constants R = m.Const(value=1.9858775e-3) # Gas constant [kcal/mol*K] # Final Time = FV tf = m.FV(value=1,lb=0.1,ub=20) tf.STATUS = 1 # MV T = m.MV(value=425, ub=475, lb=425) # degC T.STATUS = 1 T.DCOST = 0 # Variables x1 = m.Var(value = 1) # kerogen x2 = m.Var(value = 0) # pyrolytic bitumen x3 = m.Var(value = 0) # oil and gas x4 = m.Var(value = 0) # carbon residue p = np.zeros(nt) p[-1] = 1.0 final = m.Param(value=p) # Parameters # Frequency factor a1 = m.Param(value=np.exp(8.86)) a2 = m.Param(value=np.exp(24.25)) a3 = m.Param(value=np.exp(23.67)) a4 = m.Param(value=np.exp(18.75)) a5 = m.Param(value=np.exp(20.7)) # Activation envergy [Kcal/g-mole] b1 = m.Param(value=20.3) b2 = m.Param(value=37.4) b3 = m.Param(value=33.8) b4 = m.Param(value=28.2) b5 = m.Param(value=31.0) # Intermediates k1 = m.Intermediate(a1 * m.exp(-b1/(R*(T+273.15)))) k2 = m.Intermediate(a2 * m.exp(-b2/(R*(T+273.15)))) k3 = m.Intermediate(a3 * m.exp(-b3/(R*(T+273.15)))) k4 = m.Intermediate(a4 * m.exp(-b4/(R*(T+273.15)))) k5 = m.Intermediate(a5 * m.exp(-b5/(R*(T+273.15)))) # Equations m.Equation(x1.dt()/tf == -k1*x1 - (k3 + k4 + k5) * x1*x2) m.Equation(x2.dt()/tf == k1*x1 - k2*x2 + k3*x1*x2) m.Equation(x3.dt()/tf == k2*x2 + k4*x1*x2) m.Equation(x4.dt()/tf == k5*x1*x2) # Objective function m.Obj(-final*x2) m.options.SOLVER = 3 m.options.IMODE = 6 m.solve() plt.figure(1) tm = m.time * tf.value[0] plt.subplot(3,1,1) plt.plot(tm,x1.value,'k:',LineWidth=2,label=r'$x_1$=Kerogen') plt.plot(tm,x2.value,'b-',LineWidth=2,label=r'$x_2$=Pyrolytic Bitumen') plt.ylabel('Fraction') plt.legend(loc='best') plt.subplot(3,1,2) plt.plot(tm,x3.value,'g--',LineWidth=2,label=r'$x_3$=Oil & Gas') plt.plot(tm,x4.value,'r-.',LineWidth=2,label=r'$x_4$=Carbon Residue') plt.ylabel('Fraction') plt.legend(loc='best') plt.subplot(3,1,3) plt.plot(tm,T.value,'r-',LineWidth=2,label='Temperature') plt.legend(loc='best') plt.xlabel('Time') plt.ylabel(r'Temp ($^o$C)') plt.show()
A solution is calculated with an objective function value of 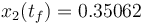 .
.