Controlled Heating (FEniCS/Casadi)
From mintOC
Revision as of 23:20, 12 January 2016 by MirkoHahn (Talk | contribs) (Created page with "This page contains a discretized version of the PDE constrained optimization problem Controlled Heating in [http://www.casadi.org CasADi 2.4.3] format. The weak version of...")
This page contains a discretized version of the PDE constrained optimization problem Controlled Heating in CasADi 2.4.3 format. The weak version of the problem was discretized using finite element methods (via FEniCS) using first-degree Lagrangian elements on a mesh automatically generated using FEniCS' mesh generation component.
CasADi
from dolfin import * import mshr import numpy import scipy, scipy.sparse import casadi # Converts FEniCS matrix to scipy.sparse.coo_matrix def matrix_to_coo(A, shape=None): nnz = A.nnz() col = numpy.empty(nnz, dtype='uint64') row = numpy.empty(nnz, dtype='uint64') val = numpy.empty(nnz) if shape is None: shape = (A.size(0), A.size(1)) it = 0 for i in range(A.size(0)): col_local, val_local = A.getrow(i) nnz_local = col_local.shape[0] col[it:it+nnz_local] = col_local[:] row[it:it+nnz_local] = i val[it:it+nnz_local] = val_local[:] it += nnz_local return scipy.sparse.coo_matrix((val, (row, col)), shape=shape) # Construct a high-resolution mesh of the unit circle domain = mshr.Circle(Point(0.0, 0.0), 1.0) mesh = mshr.generate_mesh(domain, 100) # Define the function space V = FunctionSpace(mesh, 'CG', 1) # Define trial and test functions h = TrialFunction(V) t = TrialFunction(V) v = TestFunction(V) # Construct the two parts of the constraint matrix and assemble them lhs_t = inner(grad(t), grad(v)) * dx + t * v * ds lhs_h = -h * v * dx A = matrix_to_coo(assemble(lhs_t)) B = matrix_to_coo(assemble(lhs_h)) C = casadi.DMatrix(scipy.sparse.hstack([A, B])) # Data structures for solution data sol = Function(V) control = Function(V) # Define objective functional and assemble it sol_ref = interpolate(Expression("x[0] * x[0] + x[1] * x[1]"), V) J = pow(sol_ref - sol, 2) * dx J_grad = derivative(J, sol) J_hess = derivative(J_grad, sol) c = assemble(J) g = casadi.DMatrix(numpy.concatenate((assemble(J_grad).array(), numpy.zeros(V.dim())))) H = casadi.DMatrix(matrix_to_coo(assemble(J_hess), shape=(2*V.dim(), 2*V.dim()))) # Construct CasADi problem X = casadi.MX.sym('X', V.dim() * 2) nlp = casadi.MXFunction('nlp', casadi.nlpIn(x=X), casadi.nlpOut( f=0.5*casadi.quad_form(X, H) + casadi.inner_prod(g, X) + c, g=casadi.mul(C, X) )) # Construct CasADi solver and solve problem solver = casadi.NlpSolver('solver', 'ipopt', nlp) result = solver({ 'lbx': [-numpy.inf] * V.dim() + [-10.0] * V.dim(), 'ubx': [ numpy.inf] * V.dim() + [ 10.0] * V.dim(), 'lbg': 0.0, 'ubg': 0.0 }) # Evaluate results sol.vector()[:] = result['x'][:V.dim()].toArray()[:,0] control.vector()[:] = result['x'][V.dim():].toArray()[:,0] error = Function(V) error.assign(sol_ref - sol)
Results
The solutions is calculated using IPOPT (3.12, default settings, using linear solver MUMPS on Ubuntu 15.10 for x86-64 with Linux 4.2.0-19-generic, Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-4790K CPU @ 4.00GHz, 16 GB RAM). The solution process The objective function value is 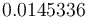 . IPOPT finds the solution in 17 iterations (62.060 seconds proc time).
. IPOPT finds the solution in 17 iterations (62.060 seconds proc time).
Solution
A Gnuplot compatible tabular version of the solution data is provided separately.